Navigating the cloud landscape can feel like finding your way through a digital jungle. But fear not! We’re here to guide you through the maze of options to find the perfect cloud provider for your unique needs. 😎
Understanding the Big Three 🌐
When it comes to cloud providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) dominate the market. Each offers a plethora of services, but how do they stack up against each other?
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Launched in 2006, AWS is the pioneer in cloud computing, offering over 200 fully-featured services from data centers globally. AWS has the largest market share and a vast ecosystem, making it a go-to choice for many organizations.
Microsoft Azure
Azure, introduced in 2010, integrates seamlessly with Microsoft’s suite of products and services. It’s particularly appealing for enterprises already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, offering strong support for hybrid cloud environments.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP, launched in 2011, leverages Google’s expertise in scalable infrastructure and data analytics. It emphasizes open-source solutions, data analytics, and machine learning capabilities, making it a favorite among data-driven organizations.
Strengths and Weaknesses ⚖️
AWS
Strengths:
- Mature Service Offerings: AWS provides a vast array of services across compute, storage, databases, analytics, networking, mobile, developer tools, management tools, IoT, security, and enterprise applications. 1
- Global Infrastructure: AWS operates in 32 geographic regions with 99 Availability Zones. This extensive global presence allows for low-latency, high-performance applications.
- Rich Ecosystem: A strong community, extensive documentation, and numerous third-party integrations make AWS highly versatile.
Weaknesses:
- Complex Pricing: With multiple pricing models and options, cost estimation can be challenging.
- Steep Learning Curve: The breadth of services can be overwhelming for newcomers.
Azure
Strengths:
- Seamless Integration with Microsoft Tools: Ideal for organizations using Windows Server, Active Directory, and other Microsoft products.
- Hybrid Cloud Solutions: Azure Stack and Azure Arc enable consistent hybrid cloud environments.
- Enterprise Agreements: Offers flexible licensing options and discounts for existing Microsoft customers.
Weaknesses:
- Service Maturity: Some services may not be as mature as AWS equivalents.
- User Interface: The Azure portal can be less intuitive, with occasional inconsistencies.
GCP
Strengths:
- Competitive Pricing: Offers sustained use discounts and committed use contracts, often making it more affordable.
- Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Strong offerings like BigQuery, Vertex AI, and TensorFlow.
- Kubernetes Leadership: Google pioneered Kubernetes, providing a highly optimized GKE service.
Weaknesses:
- Market Share: Smaller compared to AWS and Azure, leading to fewer third-party integrations.
- Enterprise Features: May lack some traditional enterprise-focused features and support.
Service-by-Service Comparison 📊
Let’s dive deeper into the core services offered by each provider.
| Service Category | AWS | Azure | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compute | EC2, Elastic Beanstalk, ECS, EKS | Virtual Machines, App Services, AKS | Compute Engine, App Engine, GKE |
| Storage | S3, EFS, FSx, Glacier | Blob Storage, Files, Disks | Cloud Storage, Persistent Disk, Filestore |
| AI & ML | SageMaker, Rekognition, Lex | Azure Machine Learning, Cognitive Services | Vertex AI, AutoML, AI Platform |
| Serverless | Lambda, Step Functions | Functions, Logic Apps | Cloud Functions, Cloud Run |
| Containers | ECS, EKS | AKS (Azure Kubernetes Service) | GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine) |
| Database | RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, SQL Server), DynamoDB | SQL Database, Cosmos DB, MySQL, PostgreSQL | Cloud SQL, Cloud Spanner, Cloud Datastore |
| Analytics | Redshift, EMR, Athena | Synapse Analytics, HDInsight | BigQuery, Dataflow, Dataproc |
| Hybrid Solutions | Outposts, Wavelength, Local Zones | Azure Stack, Azure Arc | Anthos, Bare Metal Solution |
| IoT | IoT Core, Greengrass | IoT Hub, IoT Edge | IoT Core, Edge TPU |
| Networking | VPC, Direct Connect, Route 53 | Virtual Network, ExpressRoute, Traffic Manager | VPC, Cloud Interconnect, Cloud DNS |
Detailed Insights:
- Compute Services:
- AWS EC2: Offers a wide variety of instance types, including GPU instances for high-performance computing.
- Azure Virtual Machines: Supports Windows and Linux VMs, with integration to other Azure services.
- GCP Compute Engine: Provides custom machine types for tailored performance and cost optimization.
- Storage Services:
- AWS S3: Scalable object storage with 11 nines of durability. Offers features like S3 Glacier for archival.
- Azure Blob Storage: Optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured data.
- GCP Cloud Storage: Unified object storage for live and archival data, with multi-region support.
Generative AI and LLMs 🤖
AWS: Amazon Bedrock
AWS offers Amazon Bedrock, providing access to foundation models (FMs) from AI21 Labs, Anthropic, Stability AI, and Amazon’s own Titan FMs. This service allows developers to build and scale generative AI applications without managing underlying infrastructure.
“Amazon Bedrock is the easiest way to build and scale generative AI applications with foundation models (FMs).”
Azure: Azure OpenAI Service
Azure provides the Azure OpenAI Service, enabling access to OpenAI’s powerful models like GPT-4, GPT-3, Codex, and DALL·E. It combines OpenAI’s advanced language models with Azure’s enterprise capabilities.
“Azure OpenAI Service brings together advanced language AI with Azure’s enterprise-grade capabilities.”
GCP: Vertex AI
GCP’s Vertex AI is a unified platform for machine learning. It offers tools to build, deploy, and scale ML models faster, including support for large language models (LLMs) and generative AI.
“Vertex AI makes it easier to build, deploy, and scale ML models with pre-trained and custom tooling within a unified AI platform.”
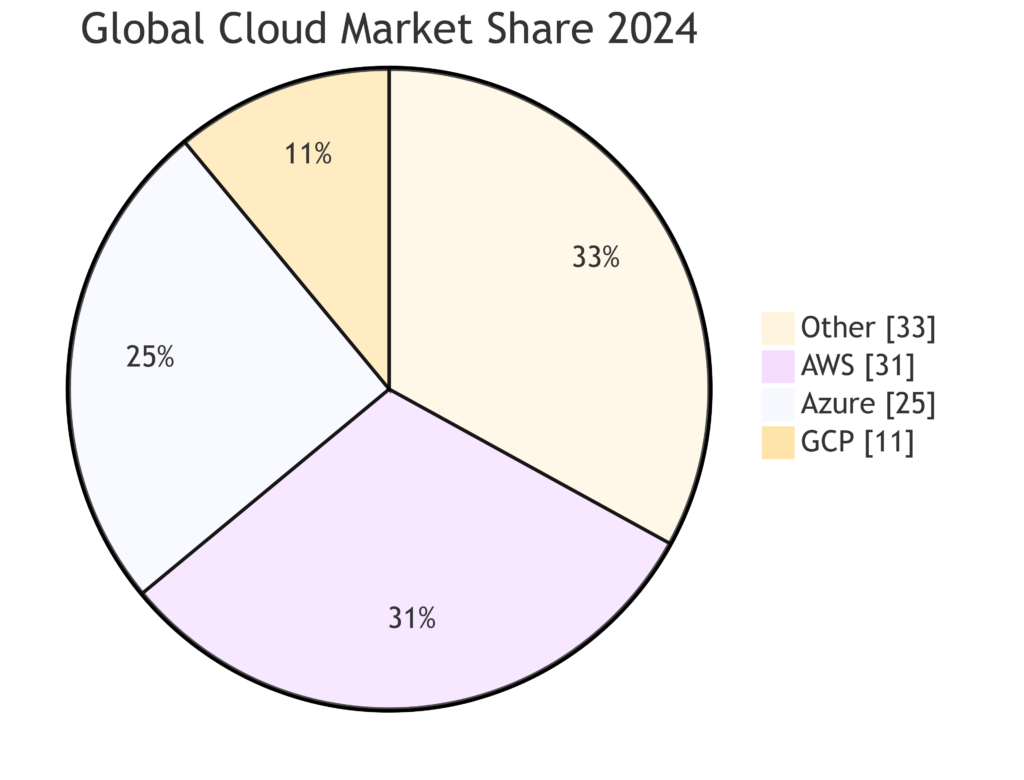
Percentages are approximate, Copyright© 2024 Towardscloud Inc.
Hybrid Architecture Solutions 🔄
As organizations transition to the cloud, hybrid architectures enable a gradual shift, integrating on-premises data centers with cloud services.
AWS: AWS Outposts and VMware Cloud on AWS
- AWS Outposts: Brings native AWS services, infrastructure, and operating models to virtually any data center or on-premises facility. It allows you to run AWS services locally while connecting to a broad range of services in the AWS Cloud.
“AWS Outposts brings native AWS services, infrastructure, and operating models to virtually any data center.” - VMware Cloud on AWS: Enables running VMware workloads on AWS infrastructure, offering seamless integration between on-premises VMware environments and AWS.
Migration Strategies:
- AWS Migration Hub: Track the progress of application migrations across multiple AWS and partner solutions.
- AWS Application Migration Service: Simplify and expedite migration from physical, virtual, or cloud infrastructure to AWS.
- AWS DataSync: Automate data transfer between on-premises storage and AWS storage services.
Azure: Azure Stack and Azure Arc
- Azure Stack: Extends Azure services and capabilities to your environment of choice—from the data center to edge locations and remote offices.
“Azure Stack is a portfolio of products that extend Azure services and capabilities to your environment of choice.” - Azure Arc: Enables management of resources across multi-cloud and on-premises environments, providing a consistent management layer.
Migration Strategies:
- Azure Migrate: Central hub for migration tools to discover, assess, and migrate workloads to Azure.
- Azure Site Recovery: Provides disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS), aiding in the migration process.
GCP: Anthos
- Anthos: A modern application management platform that provides a consistent development and operations experience across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
“Anthos lets you build and manage modern applications, anywhere.”
Migration Strategies:
- Migrate for Compute Engine: Automates the migration of VMs from on-premises or other clouds to Compute Engine.
- Transfer Appliance: Secure, high-capacity storage server for data transfer.
Cost Considerations: CAPEX vs. OPEX 💰
Understanding the financial implications of migrating to the cloud is crucial for making an informed decision. Let’s delve into the fundamentals of Capital Expenditure (CAPEX) and Operational Expenditure (OPEX) and how they relate to the cloud financial model.
Fundamentals of CAPEX and OPEX 🏦
Capital Expenditure (CAPEX)
- Definition: CAPEX refers to the funds used by an organization to acquire, upgrade, and maintain physical assets such as property, industrial buildings, or equipment.
- Characteristics:
- Upfront Costs: Significant initial investment is required.
- Depreciation: Assets depreciate over time and are accounted for over their useful life.
- Fixed Assets: Includes expenses on physical infrastructure like servers, data centers, and networking equipment.
Operational Expenditure (OPEX)
- Definition: OPEX represents the ongoing costs for running day-to-day business operations.
- Characteristics:
- Recurring Costs: Expenses occur regularly (e.g., monthly or annually).
- Flexibility: Easier to adjust based on operational needs.
- Operating Expenses: Includes costs like utilities, rent, salaries, and now, cloud service subscriptions.
CAPEX vs. OPEX in Traditional IT Infrastructure 🖥️
Traditional On-Premises Model
- CAPEX-Heavy: Requires purchasing hardware, software licenses, and building data centers.
- Long Procurement Cycles: Acquiring and setting up infrastructure can take months.
- Underutilization Risks: Fixed capacity may lead to resources being underused.
- Maintenance Costs: Ongoing OPEX for utilities, cooling, physical security, and IT staff.
Migrating to the cloud shifts expenses from CAPEX to OPEX.
Cost Comparison Table
| Cost Aspect | AWS Offerings | Azure Offerings | GCP Offerings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Models | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved Instances | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved Instances | Sustained Use Discounts |
| Cost Management | AWS Cost Explorer, Budgets | Azure Cost Management | GCP Cost Calculator |
| Migration Tools | AWS Migration Hub | Azure Migrate | Migrate for Compute Engine |
| Free Tiers | 12-Month Free Tier | 12-Month Free Services | $300 Credit for 90 Days |
The Shift to Cloud Financial Model ☁️
Cloud Computing Model
- OPEX-Focused: Cloud services are typically billed on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Reduced Upfront Costs: Eliminates the need for large initial investments in infrastructure.
- Scalability: Resources can be scaled up or down based on demand.
- Predictable Expenses: Easier to forecast operational costs with subscription models.
Benefits of OPEX Model in Cloud
- Financial Flexibility: Frees up capital for other strategic investments.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Quick provisioning of resources accelerates project deployment.
- Cost Optimization: Pay only for what you use, reducing wasteful spending.
- Innovation Enablement: Lower barriers to experimenting with new technologies.
Cloud Financial Management (FinOps) 💡
Adopting the cloud requires a new approach to financial management known as FinOps.
What is FinOps?
- Definition: A practice that brings financial accountability to cloud spending, enabling organizations to get maximum business value.
- Key Principles:
- Collaboration: Cross-functional teams work together (IT, finance, business units).
- Visibility: Real-time insights into cloud usage and costs.
- Optimization: Continuous efforts to optimize cloud spending.
Implementing FinOps
- Establish Governance: Define policies for cloud resource provisioning and usage.
- Set Budgets and Alerts: Use tools to monitor spending and receive notifications.
- Chargeback and Showback: Allocate costs to departments or projects to promote accountability.
- Optimize Resource Usage: Regularly review and right-size resources.
Cost Management Tools by Cloud Providers 🛠️
AWS Cost Management
- AWS Cost Explorer: Visualize and analyze your AWS costs and usage over time.
- AWS Budgets: Set custom cost and usage budgets and receive alerts when thresholds are exceeded.
- AWS Cost Anomaly Detection: Uses machine learning to detect unusual spending patterns.
Learn more: Azure Cost Management Documentation
- Cost Analysis: Break down costs by resource, resource group, or tags.
- Budgeting: Create budgets and monitor spending in real-time.
- Recommendations: Azure Advisor provides cost optimization suggestions.
Learn more: Azure Cost Management Documentation
GCP Cost Management
- Cloud Billing Reports: View and analyze your GCP spending.
- Budgets and Alerts: Set budgets and get notified when spending exceeds limits.
- Cost Recommendations: Identify idle resources and opportunities to save.
Learn more: GCP Cost Management
Strategic Considerations for Cloud Migration 💭
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis
- Assessment: Compare the TCO of on-premises infrastructure vs. cloud solutions.
- Include Hidden Costs: Factor in expenses like data transfer, training, and potential downtime.
- Use TCO Calculators:
- AWS: AWS TCO Calculator
- Azure: Azure TCO Calculator
- GCP: GCP Pricing Calculator
Cost Optimization Strategies
- Right-Sizing: Match resource capacity to workload demands.
- Reserved Instances/Committed Use Discounts:
- AWS: Save up to 72% with Reserved Instances.
- Azure: Save up to 72% with Reserved VM Instances.
- GCP: Save up to 57% with Committed Use Contracts.
- Spot/Preemptible Instances:
- Utilize spare capacity at significantly reduced costs for non-critical workloads.
- Auto Scaling:
- Automatically adjust resources based on real-time demand.
Impact on Financial Planning 📊
Accounting Implications
- Expense Recognition: OPEX expenses are fully deductible in the year they are incurred.
- Budgeting: Shifts focus from long-term capital budgets to operational expense planning.
Financial Ratios and Metrics
- Improved Cash Flow: Reduced CAPEX leads to better cash flow management.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Potentially faster ROI due to lower initial costs.
- Balance Sheet Impact: Lower assets and liabilities related to owned infrastructure.
Example Scenario: Traditional vs. Cloud Model 📝
Traditional On-Premises Setup
- CAPEX:
- Servers and Hardware: $500,000
- Data Center Construction: $1,000,000
- OPEX:
- Maintenance and Utilities: $150,000/year
- IT Staff Salaries: $300,000/year
Cloud-Based Setup
- CAPEX:
- Minimal upfront costs (e.g., initial setup fees)
- OPEX:
- Cloud Service Subscriptions: $400,000/year
- Reduced IT Staff Costs: $200,000/year
Outcome:
- Initial Savings: Avoidance of $1.5 million in upfront CAPEX.
- Operational Flexibility: Ability to scale expenses up or down based on usage.
- Focus on Core Business: Reallocate resources to strategic initiatives rather than infrastructure management.
Human Change Management and Certifications 🎓
Training and Certifications
AWS Certifications
- Foundational:
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
- Associate:
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate
- AWS Certified Developer – Associate
- AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate
- Professional:
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Professional
- AWS Certified DevOps Engineer – Professional
- Specialty:
- Advanced Networking
- Security
- Machine Learning
- Data Analytics
Training Resources:
- AWS Training and Certification: Offers digital and classroom training.
- AWS Skill Builder: Free digital courses to learn AWS services.
Azure Certifications
- Fundamentals:
- Azure Fundamentals (AZ-900)
- Azure Data Fundamentals (DP-900)
- Azure AI Fundamentals (AI-900)
- Associate:
- Azure Administrator Associate
- Azure Developer Associate
- Azure Security Engineer Associate
- Expert:
- Azure Solutions Architect Expert
- Azure DevOps Engineer Expert
Training Resources:
- Microsoft Learn: Free, self-paced learning paths.
- Azure Training: Instructor-led training and certification paths.
GCP Certifications
- Associate:
- Cloud Engineer
- Professional:
- Cloud Architect
- Cloud Developer
- Data Engineer
- Cloud DevOps Engineer
Training Resources:
- Google Cloud Training: Courses and hands-on labs.
- Google Cloud Skills Boost: Interactive learning platform for hands-on experience.
Managing the Human Element
- Training Programs: Implement structured training plans for staff to acquire necessary skills.
- Certification Incentives: Encourage employees to get certified by offering incentives.
- Change Champions: Identify key personnel who can advocate for the change and assist others.
- Communication Plans: Regular updates and open forums to address concerns and feedback.
- Cultural Shift: Foster a culture that embraces innovation, continuous learning, and adaptability.
Conclusion 🏁
Choosing the right cloud provider depends on your organization’s specific needs, existing infrastructure, expertise, and strategic goals. AWS offers a vast range of services and a mature platform, Azure provides seamless integration with Microsoft tools and strong hybrid solutions, and GCP excels in data analytics and machine learning capabilities.
Consider factors like service offerings, cost structures, hybrid capabilities, and the human element when making your decision. Remember, the goal is not just to migrate to the cloud but to leverage its full potential to drive innovation and efficiency in your organization. 🌟
Feel like a cloud expert yet? 😄☁️
Footnotes
AWS Product Offerings ↩
Azure Virtual Machines Documentation ↩
GCP Compute Engine Documentation ↩
GCP Cloud Storage Documentation ↩
AWS Migration Hub Documentation ↩